РОССИЯ ВНЕСЛА В ООН ПРОЕКТ КОНВЕНЦИИ КОТОРАЯ КОСНЁТСЯ КРИМИНАЛЬНОГО ИСПОЛЬЗОВАНИЯ КРИПТОВАЛЮТ
27 июля, Россия внесла в ООН проект конвенции о противодействии использованию информационно-коммуникационных технологий в преступных целях. Это первый проект документа по борьбе с киберпреступностью...
Как сообщили корреспонденту "РГ" в пресс-службе Генпрокуратуры, межведомственная российская делегация во главе с заместителем Генерального прокурора РФ Петром Городовым на встрече в штаб-квартире ООН в Вене с исполняющим обязанности исполнительного директора Управления ООН по наркотикам и преступности Деннисом Чатчавалитом официально внесла российский проект конвенции о противодействии использованию информационно-коммуникационных технологий в преступных целях. Копия проекта конвенции передана председателю специального комитета ООН по разработке конвенции о противодействии использованию информационно-коммуникационных технологий в преступных целях Фаузие Мебарки.
Таким образом, как отметили в надзорном ведомстве, Россия стала первой страной, разработавшей и представившей в спецкомитет проект универсальной конвенции, посвященной противодействию информационной преступности. Проект учитывает современные вызовы и угрозы в сфере международной информационной безопасности, в том числе, криминальное использование криптовалюты. А также вводит новые составы преступлений, совершаемых с использованием ИКТ - распространение фальсифицированной медицинской продукции, оборот наркотиков, вовлечение несовершеннолетних в совершение противоправных деяний, опасных для их жизни и здоровья, и другие. Также проект расширяет сферу международного сотрудничества в вопросах выдачи и оказания правовой помощи по уголовным делам, включая выявление, арест, конфискацию и возврат активов.
Как напомнили в Генпрокуратуре, в прошлом году в связи с взрывным ростом киберпреступности во всем мире по решению Генерального прокурора Игоря Краснова была создана межведомственная рабочая группа по противодействию информационной преступности. Одной из главных задач, поставленных перед экспертами этой группы, стала разработка проекта универсальной всеобъемлющей международной конвенции о противодействии использованию информационно-коммуникационных технологий (ИКТ) в преступных целях.
Источник: Российская Газета
РОССИЙСКИМ ЭКСПОРТЁРАМ ДАЁТСЯ ПРАВО РАЗМЕЩАТЬ ВАЛЮТНУЮ ВЫРУЧКУ НА СЧЕТАХ ИНОСТРАННЫХ БАНКОВ
27 июня В.В. Путин подписал закон, который снимает все препятствия для экспорта... Официальное название документа: Федеральный закон от 28.06.2021 № 223-ФЗ «О внесении изменений в Федеральный закон «О валютном регулировании и валютном контроле».
Суть закона в том, что российским экспортёрам золота, металлов, зерна даётся право размещать валютную выручку от экспортных продаж за рубежом, на счетах иностранных банков. То есть вывести за границу золото — получить выручку — положить её в зарубежный банк и распоряжаться ею по своему усмотрению, как своей собственностью...
Речь идёт не о каких-то мелочных сделках, а о суммах астрономических. Например, российского золота в прошлом году продали 320 тонн, металлов — на сумму 35 млрд долларов и на 8,5 млрд долларов — хлеба. К 2024 году, по планам правительства, несырьевой экспорт должен вырасти до 250 млрд долларов, или 18,5 трлн рублей (годовой бюджет). Все эти средства по новому закону останутся за границей. Апологеты этой идеи говорят, что это облегчит операции и увеличит российский экспорт. Но только зачем? Облегчить жуликам-экспортёрам вывозить капиталы за рубеж, а ограбленная страна будет продолжать балансировать на прожиточном минимуме и минимальном бюджете?
До принятия этого закона экспортёры обязаны были зачислять как рублёвую, так и валютную выручку на свои счета в российских банках. За каждый день просрочки компания должна была платить штраф 1/150 ключевой ставки ЦБ, штраф за невозврат — 75-100% от суммы сделки. По действовавшему до 1 июля законодательству нерепатриация выручки в особо крупном размере наказывалась лишением свободы на срок до пяти лет. Теперь все эти меры отменяются, а все бывшие преступники становятся добропорядочными предпринимателями.
К открытому грабежу страны шли долго. Сначала была отменена обязательная (даже частичная) продажа валютной выручки экспортёрами за рубли. Оставили лишь обязанность ввозить валютную выручку в Россию, размещать её на счетах уполномоченных российских банков. А поскольку ограничения на экспорт капитала были также отменены, то эту валюту можно было потом опять выводить за рубеж. Теперь отменили и обязательную репатриацию валютной выручки в Россию.
Отныне без репатриации выручки можно будет экспортировать медь, никель, в том числе необработанный, а также алюминий, свинец, цинк и олово, за исключением отдельных видов продукции военного назначения.
Кроме этого, согласно закону, оставлять выручку в западных банках смогут экспортёры чёрных металлов (за исключением отходов, лома и шихтовых слитков), а также металлургической продукции (кроме железнодорожных рельсов). По итогам прошлого года, по данным таможенной статистики, экспорт металлов составил 35,5 млрд долларов (10,5% всех экспортных доходов).
Если ежегодный вывоз капитала из России был в среднем около 50 млрд долларов, то с помощью нового закона он увеличится в 3—5 раз.
Вывозят золото, хлеб, металлы, нефть, газ... Строят новые дороги и мосты, чтобы вывозить больше. Вывозят деньги, распродают государственную собственность. Миллионами гектаров сжигают леса, паводковыми водами затапливают города и сёла. Ежегодно сотнями тысяч уничтожаются малые и средние предприятия, закрываются школы и больницы. Из России выжимают талантливых людей и наводняют бесталанными мигрантами. И везде воровство, грабёж, коррупция, безответственность, непрофессионализм...
Источник: Официальный сайт газеты Правда
CYBER RESILIENCE FACTORS AT BIT URAL 2021
Just three days before the long-awaited VII conference BIT Ural 2021, organized by the Association of Chiefs Information Security Officer (ACISO), which will take place on April 23 at the Yeltsin Center (after 2 years of separation). The event was organized in strict accordance with the requirements of the prevention of the spread of coronavirus infection.
The theme of the conference will be the factors of ensuring cyber resilience: people and technology. The meeting will be opened by the Chairman of the Board of ACISO, and the Director of the Department of Informatization and Communication of the Sverdlovsk Region will deliver a welcoming speech. Also, leading experts will share their work experience. A round table with the participation of FSTEC (Federal Service for Technical and Export Control), the Bank of Russia and conference partners is also planned.
Key points for discussion: trusted environment - the basis of information security; import substitution vs import matching; domestic vs foreign technologies; certification is a panacea for security or a bluff; CII requirements that people or technology come first; the trend of transition to domestic technologies - myth or reality; GSCSICA (Global System for Collecting and Sharing Information about Computer Attacks - will the market expectations be met.
Source: aciso.timepad.ru
EUROPOL RELEASED ITS SERIOUS AND ORGANISED CRIME THREAT ASSESSMENT 2021
12 Apr 2021, Europol publishes the European Union (EU) Serious and Organised Crime Threat Assessment, the EU SOCTA 2021. The SOCTA, published by Europol every four years, presents a detailed analysis of the threat of serious and organised crime facing the EU. The SOCTA is a forward-looking assessment that identifies shifts in the serious and organised crime landscape.
The SOCTA 2021 details the operations of criminal networks in the EU and how their criminal activities and business practices threaten to undermine our societies, economy and institutions, and slowly erode the rule of law. The report provides unprecedented insights into Europe’s criminal underworld based on the analysis of thousands of cases and pieces of intelligence provided to Europol.
The SOCTA reveals a concerning expansion and evolution of serious and organised crime in the EU. The document warns of the potential long-term implications of the COVID-19 pandemic and how these may create ideal conditions for crime to thrive in the future. The report clearly highlights serious and organised crime as the key internal security challenge currently facing the EU and its Member States.
Launched at the Portuguese Police’s headquarters (Policia Judicária) in Lisbon during the Portuguese Presidency of the Council of the European Union, the SOCTA 2021 is the most comprehensive and in-depth study of serious and organised crime in the EU ever undertaken.
THE MOST PRESSING INTERNAL SECURITY THREAT TO THE EU
EU citizens enjoy some of the highest levels of prosperity and security in the world. However, the EU still faces serious challenges to its internal security, threatening to undo some of our common achievements and undermine shared European values and ambitions. As the EU is facing the COVID-19 pandemic, one of the most significant crises since the end of World War II, criminals seek to exploit this extraordinary situation targeting citizens, businesses, and public institutions alike.
The analysis presented in the SOCTA 2021 highlights key characteristics of serious and organised crime such as the widespread use of corruption, the infiltration and exploitation of legal business structures for all types of criminal activity, and the existence of a parallel underground financial system that allows criminals to move and invest their multi-billion euro profits.
Serious and organised crime encompasses a diverse range of criminal phenomena ranging from the trade in illegal drugs to crimes such as migrant smuggling and the trafficking in human beings, economic and financial crime and many more.
Key findings of the SOCTA 2021:
- Serious and organised crime has never posed as high a threat to the EU and its citizens as it does today.
- The COVID-19 pandemic and the potential economic and social fallout expected to follow threaten to create ideal conditions for organised crime to spread and take hold in the EU and beyond. Once more confirmed by the pandemic, a key characteristic of criminal networks is their agility in adapting to and capitalising on changes in the environment in which they operate. Obstacles become criminal opportunities.
- Like a business environment, the core of a criminal network is composed of managerial layers and field operators. This core is surrounded by a range of actors linked to the crime infrastructure providing support services.
- With nearly 40 percent of the criminal networks active in drugs trafficking, the production and trafficking of drugs remains the largest criminal business in the EU.
- The trafficking and exploitation of human beings, migrant smuggling, online and offline frauds and property crime pose significant threats to EU citizens.
- Criminals employ corruption. Almost 60% of the criminal networks reported engage in corruption.
- Criminals make and launder billions of euros annually. The scale and complexity of money laundering activities in the EU have previously been underestimated. Professional money launderers have established a parallel underground financial system and use any means to infiltrate and undermine Europe’s economies and societies.
- Legal business structures are used to facilitate virtually all types of criminal activity with an impact on the EU. More than 80% of the criminal networks active in the EU use legal business structures for their criminal activities.
- The use of violence by criminals involved in serious and organised crime in the EU appears to have increased in terms of the frequency of use and its severity. The threat from violent incidents has been augmented by the frequent use of firearms or explosives in public spaces.
- Criminals are digital natives. Virtually all criminal activities now feature some online component and many crimes have fully migrated online. Criminals exploit encrypted communications to network among each other, use social media and instant messaging services to reach a larger audience to advertise illegal goods, or spread disinformation.
The SOCTA 2021 assists decision-makers in the prioritisation of serious and organised crime threats. It is a product of close cooperation between Europol, EU Member States law enforcement authorities, third parties such as EU agencies, international organisations, and countries outside the EU with working arrangements with Europol. These crucial stakeholders’ involvement is also reflected in the SOCTA’s role as the cornerstone of the European Multidisciplinary Platform Against Criminal Threats (EMPACT) in the EU.
BLOCKCHAIN & BITCOIN CONFERENCE MOSCOW IS BACK!
Event on the Prospects of Crypto Market and the Use of Blockchain in Business Will Take Place in April 2021.
Bitcoin rate is breaking records, the world community is actively discussing the development of tokenization, and the law on digital financial assets and digital currency came into force in Russia. Within the new conditions, crucial questions appear: how to gain income on the rising trend of electronic money and what is the future of the cryptocurrency market?
To discuss these and other topics, Smile-Expo will host the ninth Blockchain & Bitcoin Conference Moscow 2021 on April 6! The event is dedicated to the prospects of making money on cryptocurrency and the specifics of regulating the circulation of digital assets.
Event will unite top-notch industry professionals: financial analysts, economists, lawyers, representatives of technological companies, developers of innovative platforms and others.
Event program
Events under Blockchain & Bitcoin Conference brand have been held in Moscow since 2014. During this time, they managed to gather thousands of guests. Traditionally, specialized events unite leading industry representatives. The ninth conference will delight visitors with an even richer program and the most useful theme-specific blocks.
Blockchain & Bitcoin Conference Moscow 2021 features meaningful presentations from multidisciplinary experts, a demo zone with advanced products and services, panel discussion, speed dating and effective networking.
Speakers will focus on the main trends in the digital assets industry, legal aspects of regulation and promising ways to make money on the crypto market.
Topics that will be considered at the conference include:
- NFT as a new class of digital assets: Features of non-fungible tokens.
- Mining possibilities: How to mine cryptocurrency and make a profit?
- Cryptotrading as a way to make money: Specifics and efficient strategies.
- Legislative regulation of cryptocurrencies: How the market will change in 2021.
Demo area will be arranged at the event, where niche companies will present their best solutions. Representatives of exhibitors will be happy to answer all questions from guests and discuss the benefits of possible cooperation.
Conference guests will have the opportunity to find investors or business partners, as well as exchange experience and knowledge. Join us!
Meet the first speakers of Blockchain & Bitcoin Conference Moscow 2021
Leonid Bugaev is a business mentor, a specialist in the field of networking and online marketing. Vice President of Communications at Chatex. Provides personal and corporate consultations for Microsoft, Toyota, Gazprom Neft, Beeline, MTS, MegaLabs, etc. Author of books and Mobility for business method.
The speaker will cover the topic “How decentralized systems are created. The rise of Web 3.0”.
Daria Barkova is the co-founder and Head of HR department at Unicorn Search IT center. More than 7 years of experience in recruiting. Searches for fintech, blockchain, gamedev developers and helps companies to attract real stars of the IT industry to the team.
At the conference, Daria will present a report on the topic “Finding staff for blockchain development: Problems, best practices”.
Blockchain & Bitcoin Conference Moscow 2021 will feature a panel discussion on the topic “Legal implications of the law on digital financial assets” Meet its participants:
• Andrey Tugarin – expert in the field of intellectual property rights protection, patent attorney of the Russian Federation. Partner and Director of GMT Legal that provides legal support for crypto projects. Member of the International Trademark Association (INTA) and the Federation of Patent Agents (FICPI).
• Yanina Petrovskaya – lawyer, advisor at RLP Lawyers Liechtenstein. Provides services for legal support of blockchain projects. Member of Capital Market and Technology Association that creates standards for assets tokenization. Yanina is a lecturer at Blockchain Lawyers (BCL) – supplementary education program.
• Sarkis Darbinyan is a lawyer in cyber rights protection, partner of Digital Rights Center and Digital Rights Laboratory. Co-founder of RosComSvoboda public project. The speaker is a member of the working group Communications and IT at the Expert Council under the Government of the Russian Federation.
• Maria Agranovskaya – specialist in digital currency regulation, lawyer. Managing Partner, Head of the Fintech, Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies Practice at GRAD Moscow Bar Association. Has expertise in the legal aspects of creating investment mechanisms, funds, trusts, holdings, asset restructuring.
The full list of speakers can be found on the official website.
Special offer!
Celebrating the Defender’s Day, we launch a special promotion: from 17 to 24 of February, Conference category tickets can be purchased with a 30% discount!
Ticket price during the promotion is 7,000 RUB.
Ticket price from February 25 – 10,000 RUB.
The offer is valid for 8 days only. The early bird period will last until February 28, and starting from March 1, the cost of tickets will increase to 15,000 RUB.
Blockchain & Bitcoin Conference Moscow 2021 will be organized by Smile-Expo international company that has been conducting business events in the field of innovations for 15 years.
Tickets to the event are already on sale! Register on the official conference website to attend main event in the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain!
Program and registration - moscow.bc.events
$ 400M INVESTMENT SCAM - FENITA LA COMEDY FINIKO
The illegal Finiko service started operating at the end of 2017. It was positioned as an automatic profit-making system. Currently, it is represented by Cyfron FNK LTD, registered in the state of Saint Lucia (no license is required to work with cryptocurrencies).
The site in the .ru domain zone is not available. There is a working mirror of “thefiniko” (in the .com zone). The user agreements on both sites are identical. What is noteworthy is that the platform offers gaming programs that mimic investment programs. And the internal CFR token is not an official currency and has no financial value. The company does not bear any responsibility.
This approach allows Finiko to work without loss since 2017. In November 2018, the platform launched an active advertising campaign. The scammers offered to buy an apartment or a car, pay off another loan for 35% of the cost. The peak of active use of the service occurred at the end of 2019. This was accompanied by the visibility of the accrual of funds to users. However, few users were able to withdraw real funds...
There are the main signs of a financial pyramid: lack of regulation, registration in an offshore company, short life (the cost of the CFR token is close to zero), very high profitability (promised more than 200% per year), enticing and expensive website design, a lot of good reviews.
Finiko, the only known cryptocurrency, has a huge number of wallets in Bitcoin and Ethereum. The largest crypto wallet received 12099.294 BTC (almost in 2.5 years). It may have been used for trading on the stock exchange. More than 129 thousand wallets involved in the activities of the illegal service have been identified. The main large (used for receiving / sending) wallets are monitored by the services of the SICP platform.
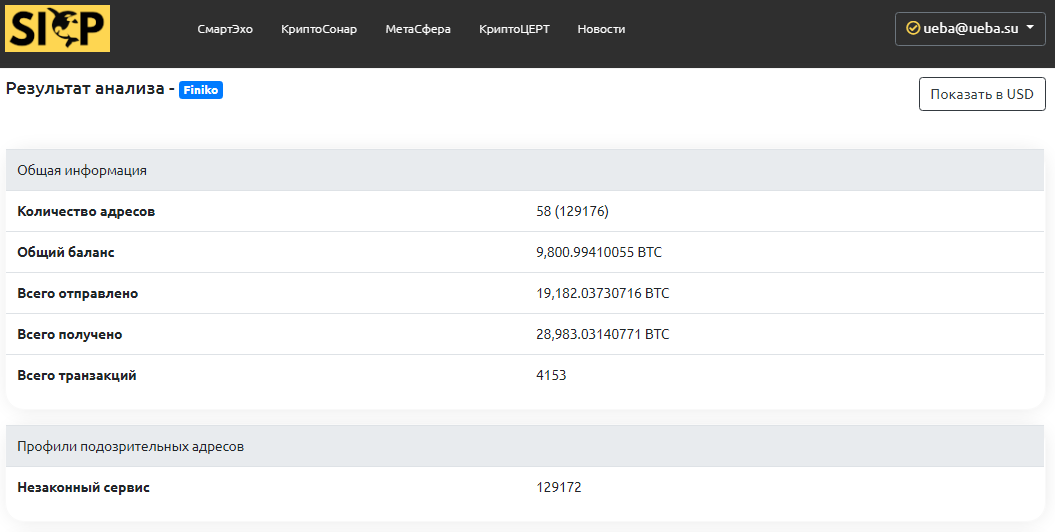
In the darknet, there is a forum where enthusiasts are working to identify large Finiko wallets and select private keys to them. In total, Finiko attracted more than $300 million from the population (according to SICP experts, more than $400 million)!..
Analysis of recent transactions shows that the funds are withdrawn mainly on the Asian cryptocurrency exchange, managed from Russia. If you or your loved one suffered from the activities of Finiko, please contact CryptoCERT (This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.).
Source: sicp.ueba.su
ADDED CUSTODIAN XAPO CRYPTOCURRENCY WALLETS
Users of the SICP platform have access to a pool of Xapo wallet addresses for analysis, with user marks of owners (the largest received 231,834.287 BTC), which was launched in the jurisdiction of Hong Kong in 2013. Already in 2014, support for debit cards for operations with cryptocurrencies was implemented. In 2015, the headquarters was moved from the USA to Switzerland.
In August 2019, Coinbase acquired the Xapo custodian (for about $ 55 million). Thus, Xapo came under the control of Coinbase Custody, making the relatively young custodian of the crypto exchange the world's largest storage of cryptocurrencies by capitalization. Today, he holds over $ 7 billion for over 120 large clients in 14 countries.
In 2020, the company moved its operations from California to Gibraltar, which offers a regulatory framework for cryptocurrency companies. The changes in Xapo come amid litigation after the custodian was accused of circulating stolen funds…
So, according to a lawsuit filed by German citizen D. Novak, Xapo and the Indodax cryptocurrency exchange contributed to the turnover of stolen cryptocurrencies. It also reveals that Xapo holds 19.99 BTC from the stolen assets, and the Indodax exchange has 476.69 BTC.
By the end of 2020, the crypto custodian (owned by crypto exchange Coinbase) plans to restructure its business and become a digital bank. Represented by legal entities in the United States (Xapo Blockchain Limited) and Gibraltar (Xapo Gibraltar Limited) and meets the regulatory requirements for financial services, virtual asset providers, electronic money and security.
Source: Xapo
ADDED COINPAYMENTS EXCHANGE CRYPTOCURRENCY WALLETS
CoinPayments payment system was launched in Estonia in 2013. The electronic wallet of the payment system is used by a large number of sellers and buyers in more than 180 countries, as the wallet supports more than 2005 tokens. The payment system received a regional license to work. However, the withdrawal function to fiat currency is not available.
Over the past 2-3 years, information has been received that cybercriminals have discovered a vulnerability that allows them to withdraw more funds than were in the account. Then the administration of the service compensated for the damage to half of the victims. Also, the site stopped working, which affected a large number of complaints from users and led to problems in investment projects of clients.
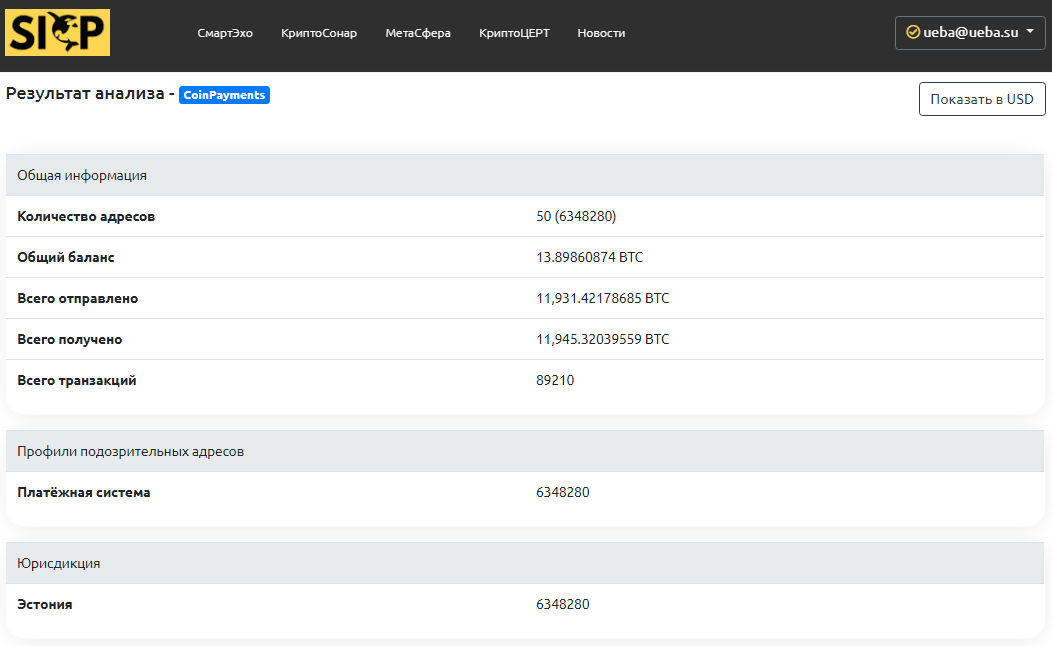
CoinPayments also supports the issuance of prepaid cards with a deposit in cryptocurrencies (over 100 types). Such cards can be used in various jurisdictions and carry significant risks of money laundering. There is an official website in the TOR network.
Source: CoinPayments
5TH ISSUE INFORMATION SECURITY MAGAZINE: SPECIAL PROJECT SOC
On November 25, 2020, the long-awaited 5th issue of the SOC magazine was released. Special issue project: SICP platform for tracking suspicious transactions and ensuring blockchain security.
The article says that the field of cryptocurrencies is technically more complex than traditional finance, noticeably more decentralized and less controllable. Therefore, tools are required to help the use of cryptocurrencies in a legal manner and for legitimate purposes. At the same time, the main systemic problem associated with the use of cryptocurrencies is the possibility of their use for illegal operations, in particular for the legalization of criminal income, as well as for financing prohibited activities.
Also, the services of the Russian platform are considered, the peculiarities of their functioning in the Russian realities. The most detailed descriptions of the recently launched CryptoCERT service. Combined with the threats and risks inherent in digital assets...
Source: Information Security
Magazine: ITSec.ru
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SECURITY SAINT PETERSBURG 2020
In 5 days, the conference on Information Technology Security (BIT St. Petersburg 2020) will take place in the Northern capital. The IX meeting will be devoted to information security and cybersecurity issues, the focus of attention will be on the discussion of CII and the implementation of the requirements of 187-FZ.
By tradition, Victor Minin (Chairman of the Board of ACISO) will deliver a welcoming speech and present a plenary report for the current year. In two sections (trends, practice), leading experts in the field of cybersecurity will share their experience. Among them, Natalia Manuylova (Chief Compliance Officer SICP) - Cryptocompliance for the security of CII, Alexander Podobnykh (CISO SICP, Special Development Department of Technopark St. Petersburg) - Digital financial assets and CII subjects, as well as other respected experts.
The conference will be held on October 15, in compliance with the requirements aimed at preventing the spread of the new coronavirus infection...
Source: BIT-Aciso
О КОСАтка
Корпоративная система аналитики Транзакция Криптовалюта Актив - кибербезопасность инфраструктуры блокчейнов и антифрод в криптовалютной сфере (антискам, прозрачность, комплаенс).
Связаться
Российская Федерация, Москва
Тел.: +7 (911) 999 9868
Факс:
Почта: cosatca@ueba.su
Сайт: www.ueba.su